Lobar Pnumonia

Mycoplasma pneumoniae also can cause pneumonia.
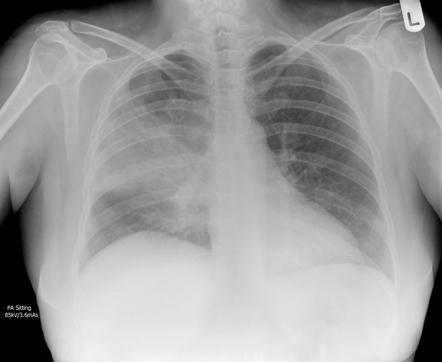
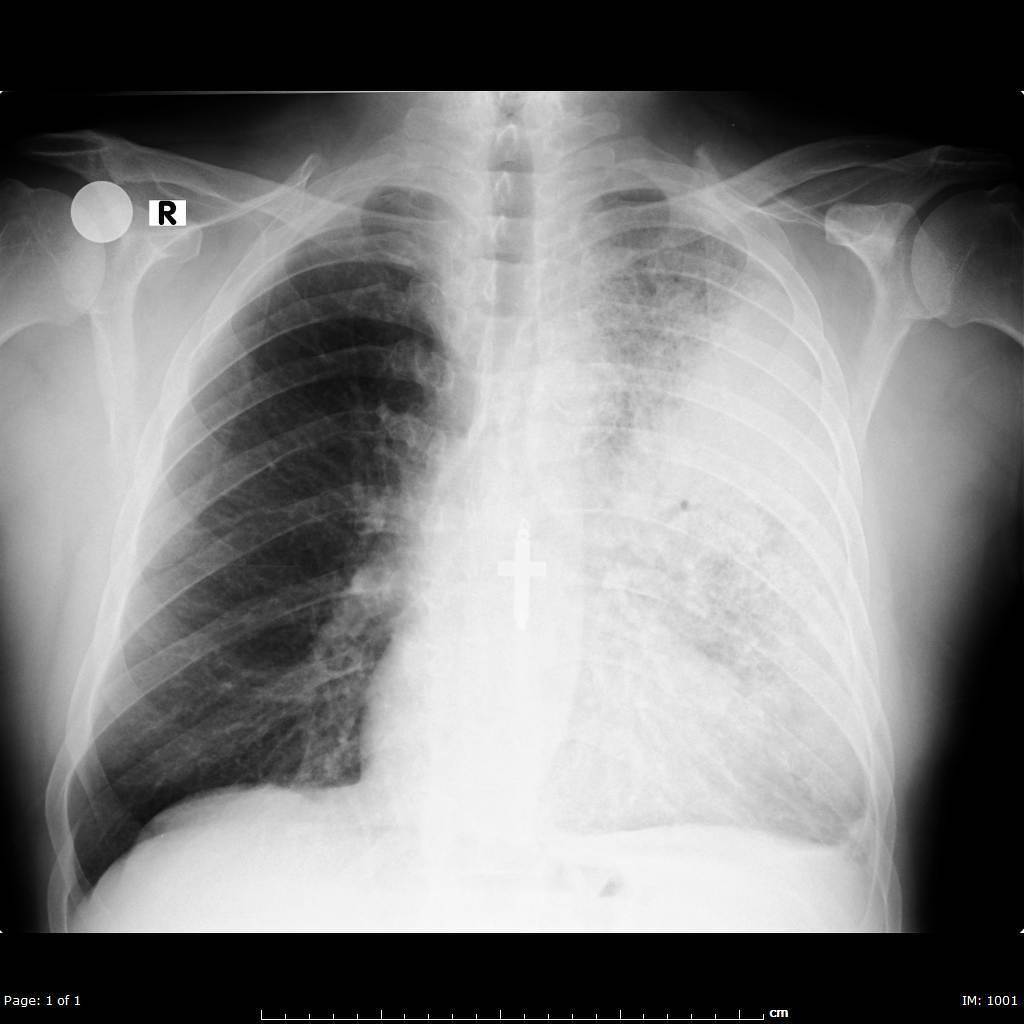
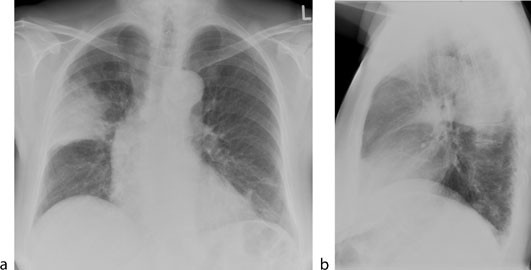
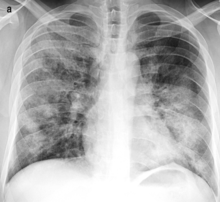
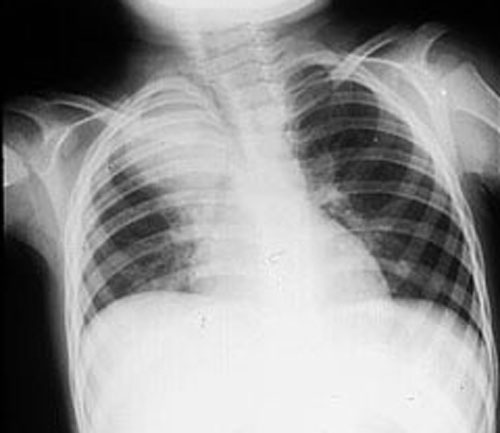
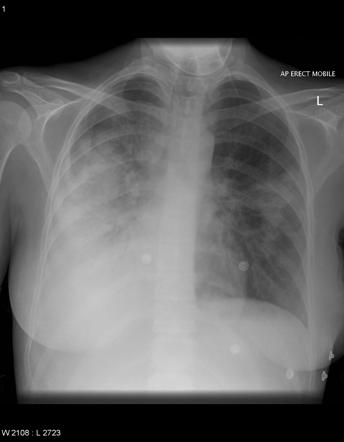
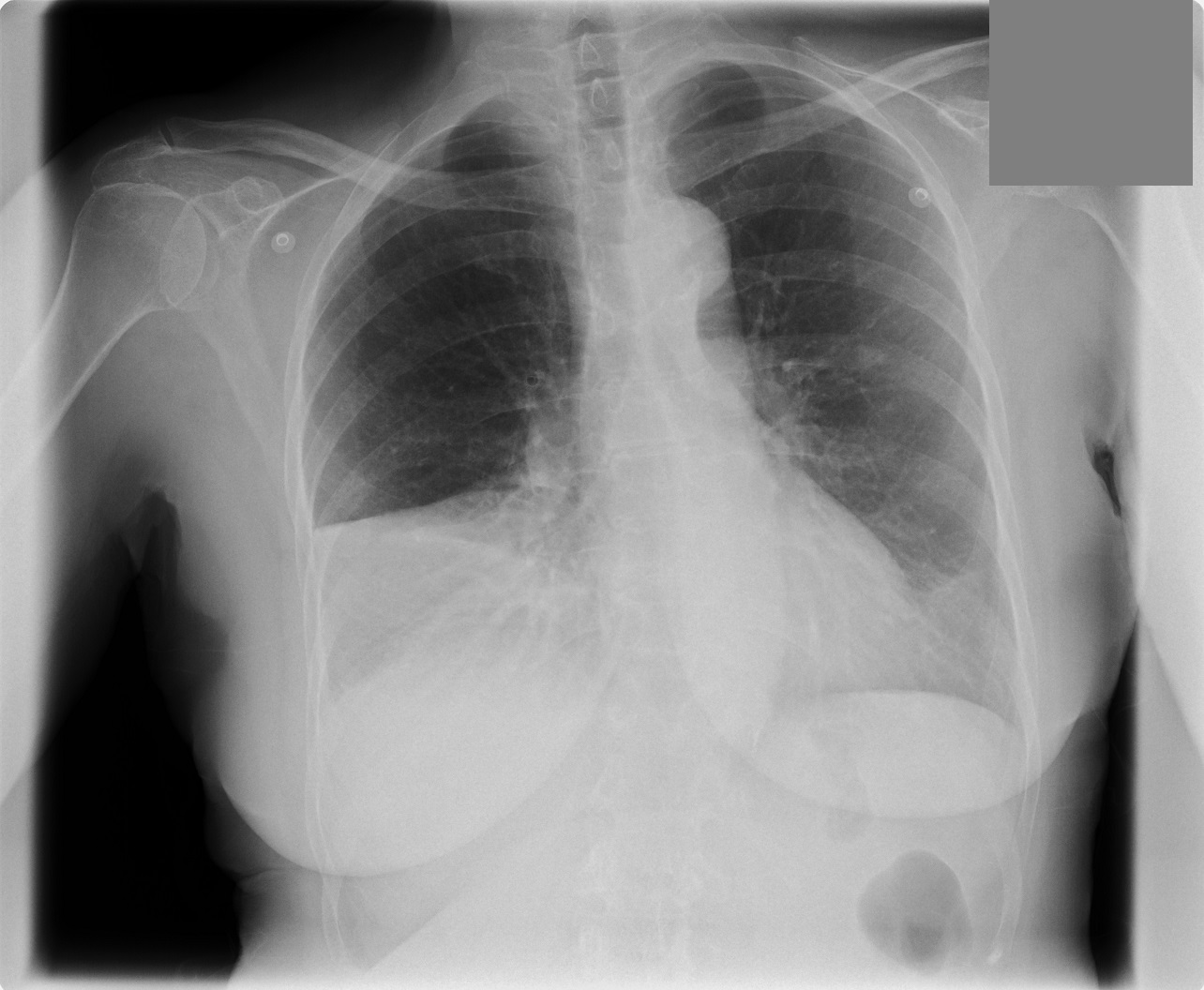
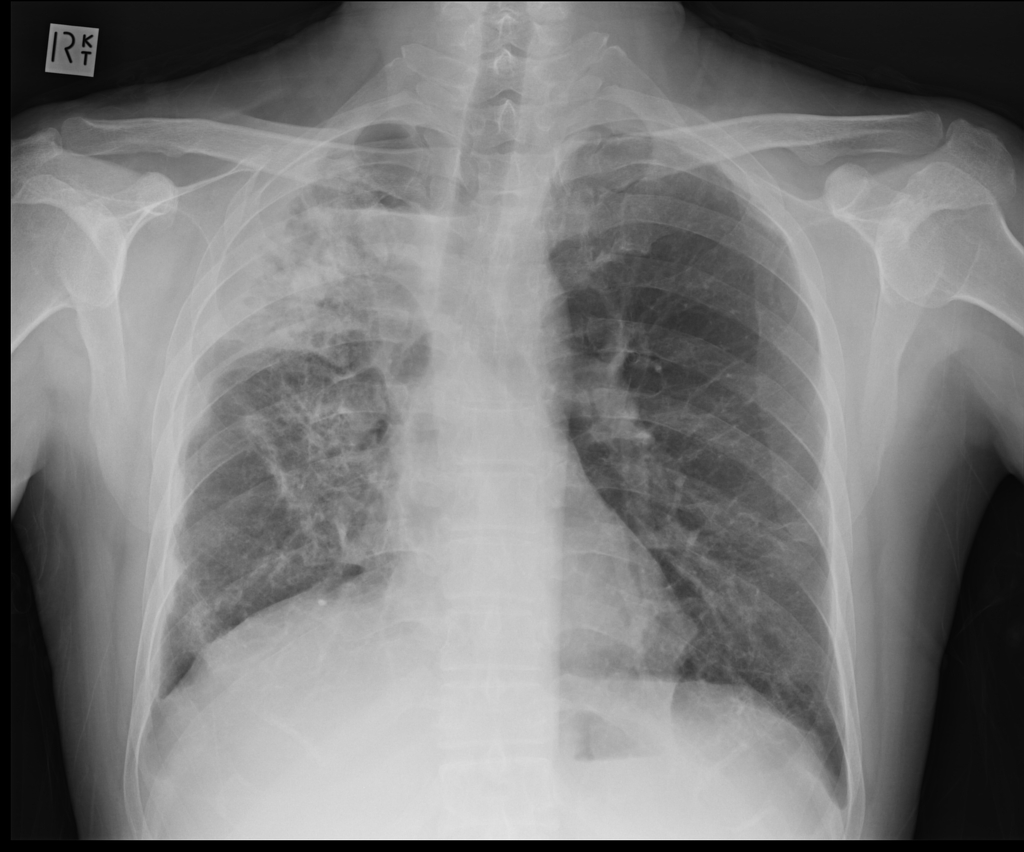
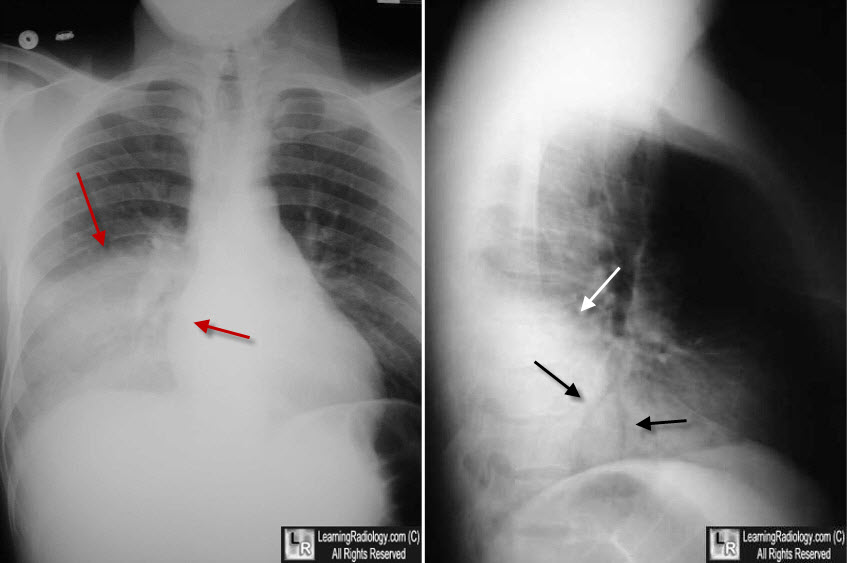
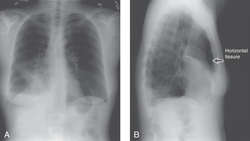
Lobar pnumonia. Lobar pneumonia refers to an acute inflammation of the lungs localized to an entire lung lobe. Lobar pneumonia references a form of pneumonia that affects a specific lobe or lobes of the lung. The most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in the u s. Figure a shows the location of the lungs and airways in the body.
Lobar pneumonia is a form of pneumonia characterized by inflammatory exudate within the intra alveolar space resulting in consolidation that affects a large and continuous area of the lobe of a lung. It happens when an infection causes the air sacs in your lungs your doctor will call them. This is a bacterial pneumonia and is most commonly community acquired. This type of pneumonia can occur on its own or after you ve had a cold or the flu.
It is mostly caused by streptococcus pneumoniae. Lobar pneumonia also known as non segmental pneumonia or focal non segmental pneumonia 7 is a radiological pattern associated with homogeneous and fibrinosuppurative consolidation of one or more lobes of a lung in response to bacterial pneumonia. Commonly due to infection by streptococcus pneumoniae. Lobar pneumonia is an acute exudative inflammation of an entire pulmonary lobe produced in 95 of cases by streptococcus pneumoniae pneumococci.
Common to all stages is the enlargement of the affected lobe with loss of it s spongy appearance. The antibiotic is chosen based on the causative organism identified or suspected. Sputum is scanty and usually of a rusty tint from altered blood. In the first stage which occurs within 24 hours of infection the lung is characterized microscopically by vascular congestion and alveolar.
In children round pneumonia develops instead because the pores of kohn which allow the lobar spread of infection are underdeveloped. When the infection is confined to only one or few lobes of lungs that is known as lobar pneumonia. It is one of three anatomic classifications of pneumonia. Pneumonia is a lung infection that can range from mild to so severe that you have to go to the hospital.
According to the localization of the inflammatory foci pneumonia is divided into two main subcategories as lobar pneumonia and bronchopneumonia. Antibiotics are almost always necessary to clear this type of pneumonia. Pulmonary disease affecting one or more lobes or part of a lobe of the lung in which the consolidation is virtually homogeneous.